Hybrid learning has emerged as a transformative learning system, blending traditional in-person instruction with the flexibility of online activities. This approach has gained momentum over the past decade, driven by the growing need for adaptable learning environments that cater to diverse preferences. Combining the interactive nature of classrooms with the vast resources available online, hybrid learning enables a personalized education experience. It empowers students to develop critical skills while offering teachers innovative methods to enhance instruction.
Hybrid learning presents a promising yet challenging educational model, requiring strong digital infrastructure and effective teaching strategies to bridge the gap between physical and virtual classrooms. Operational challenges such as teacher shortages and the need for redefined delivery methods accelerated the shift to hybrid models. Hybrid learning emerged as a balanced approach, combining in-person and remote elements, but opinions remain divided on its effectiveness. As the model evolves, educators must address these challenges and harness hybrid learning’s potential to create engaging, resilient learning experiences that prepare students for a digital future.
Understanding Hybrid Learning: A Modern Approach to Education
Hybrid learning, a revolutionary educational model, integrates personal classroom experiences with digital tools and online learning opportunities. This approach allows students to participate in various ways—attending classes in person, engaging online, or combining both.
By merging traditional teaching methods with technology, hybrid learning provides an adaptable framework that caters to diverse learning needs, whether for K-12 education, higher education, or professional training. Unlike blended learning, which focuses more on asynchronous methods, hybrid learning synchronizes face-to-face interactions with live virtual instruction, enabling teachers to simultaneously address both remote and in-classroom students.
The foundation of hybrid learning lies in its dual components:
In-person learning: This includes direct interactions such as lectures, discussions, and hands-on activities, offering immediate feedback and collaboration.
Online learning: Leverages digital platforms to deliver content, facilitate discussions, and allow for self-paced study. Tools like videos, real-time data, and virtual spaces enrich traditional lessons, making concepts more relatable.
For instance, a teacher explaining agricultural techniques in a hybrid setup might use interactive videos and case studies to illustrate real-world applications, encouraging students to brainstorm and solve region-specific challenges.
Despite its benefits, hybrid learning poses challenges like managing technological infrastructure and balancing the needs of both remote and in-person students. However, its flexibility is unmatched, making it a vital model in an era shaped by the rapid technological advancements. As the future of education evolves, hybrid learning stands out as a promising framework that equips students with the skills needed in a digital-first world while ensuring inclusivity for those unable to attend traditional classrooms.
Key Benefits of Hybrid Learning Model
Hybrid learning offers numerous advantages by integrating online and face-to-face instruction. Here are a few:
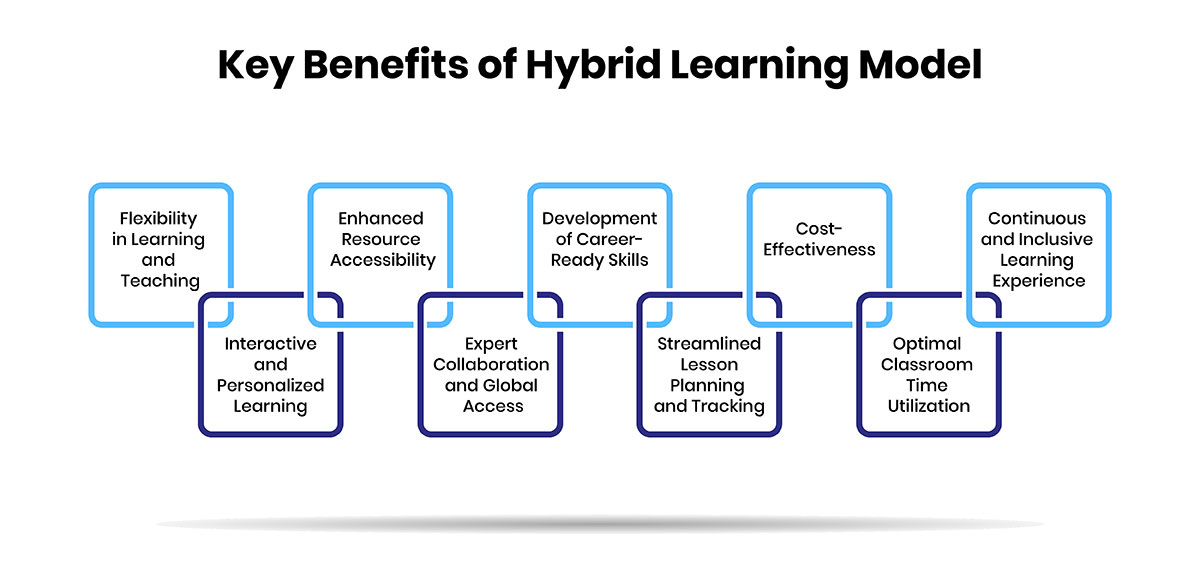
-
Flexibility in Learning and Teaching:
Hybrid learning offers flexible scheduling, allowing students to alternate between home and classroom. This flexibility benefits professionals, parents, and remote learners, while teachers can adjust strategies to reduce repetitive tasks, enhancing adaptability. -
Interactive and Personalized Learning:
Online tools and classroom activities create engaging learning experiences. Data-driven platforms tailor content to individual progress, developing personalized learning that improves outcomes. -
Enhanced Resource Accessibility:
Students can access digital resources like online libraries and virtual labs, expanding educational opportunities beyond traditional methods. Virtual labs, for example, allow students to conduct experiments remotely. -
Expert Collaboration and Global Access:
Hybrid learning connects students with global experts and institutions, democratizing education and providing access to high-quality learning, especially in rural or underserved areas. -
Development of Career-Ready Skills:
Hybrid models help students build essential skills like communication, collaboration, and digital literacy, ensuring they’re prepared for dynamic professional environments. -
Streamlined Lesson Planning and Tracking:
Digital tools aid educators in lesson planning and performance tracking, improving efficiency and allowing more focus on delivering impactful instruction. -
Cost-Effectiveness:
By reducing the need for physical infrastructure and travel, hybrid learning becomes a cost-effective option for both institutions and students, often resulting in lower tuition and expenses. -
Optimal Classroom Time Utilization:
In-person sessions focus on hands-on activities, while online learning covers theoretical lessons, maximizing teaching effectiveness and student engagement. -
Continuous and Inclusive Learning Experience:
Hybrid learning integrates online and offline methods for a continuous education flow, ensuring students can apply knowledge in practical contexts while accessing supplementary materials online.
Challenges of Hybrid Learning
While hybrid learning offers significant advantages, it also presents several challenges that must be addressed to ensure its effectiveness. Below is an overview of the key issues:
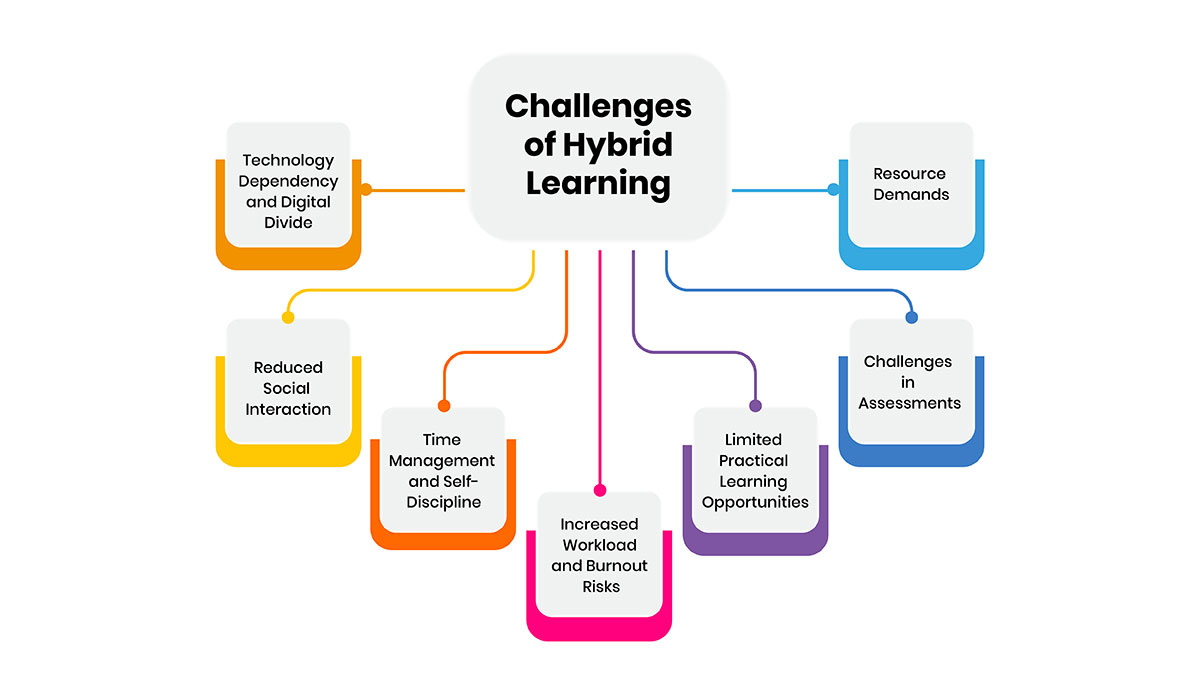
-
Technology Dependency and Digital Divide
Hybrid learning heavily relies on access to high-speed internet and digital devices, posing challenges for students from underserved communities. -
Reduced Social Interaction
Although hybrid models include face-to-face sessions, the level of social engagement often falls short of traditional classrooms. This can lead to feelings of isolation, particularly for students spending more time in virtual settings. -
Time Management and Self-Discipline
The self-paced nature of hybrid learning demands strong time-management skills. Many students, particularly those new to online education, struggle to balance tasks, which can negatively affect their academic performance. -
Increased Workload and Burnout Risks
The constant shift between online and offline modes can lead to fatigue for both students and educators. Research indicates that managing dual modalities often results in stress and burnout, especially when workloads are not balanced effectively. -
Limited Practical Learning Opportunities
Hybrid models may not adequately support hands-on training in fields like laboratory sciences or the arts, where physical interaction is crucial for skill development. Simulations, while helpful, cannot always replicate real-world experiences. -
Challenges in Assessments
Online assessments raise concerns about academic integrity and the accuracy of grading. Without robust monitoring systems, ensuring fairness and effective measurement of learning outcomes becomes challenging. -
Resource Demands
Implementing hybrid learning requires significant investment in technology infrastructure, teacher training, and ongoing support. These resources may not be readily available in all institutions, particularly in underfunded areas.
Implementing Hybrid Learning in the Classroom: A Strategic Approach
Hybrid learning, which combines both in-person and online instruction, requires careful planning and the integration of various technologies to be effective. Here’s a guide to implementing hybrid learning in the classroom:
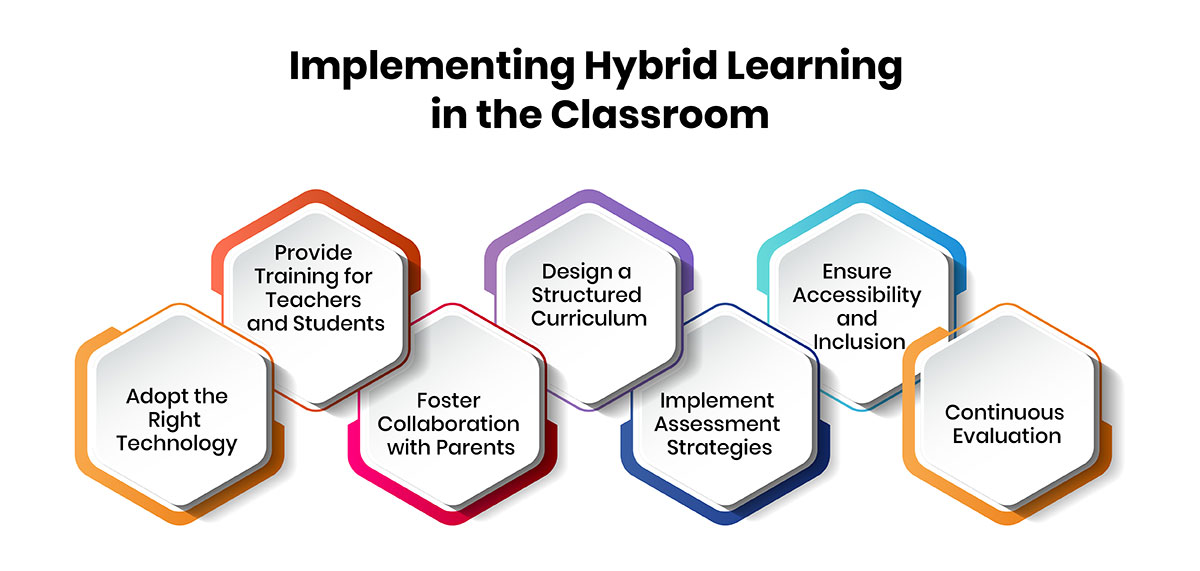
-
1. Adopt the Right Technology
To successfully integrate hybrid learning, the classroom needs to be equipped with essential technology. Key tools include:
- Intelligent Interactive Panels (IIP): These smart panels enable teachers to seamlessly conduct both in-person and online sessions with cloud-based resources and interactive features.
- Learning Management System (LMS): This platform helps manage assignments, quizzes, and communications, ensuring that both remote and in-person students are equally engaged.
- Live Broadcast Cameras and Audio: High-quality cameras with excellent audio capabilities are essential for clear communication with remote students.
- High-Speed Internet: A stable internet connection ensures smooth online learning experiences without disruptions.
-
2. Provide Training for Teachers and Students
Hybrid teaching requires educators to be comfortable with new tools and methods. Educational Institutes should offer training for teachers to become proficient with interactive panels, cameras, and LMS platforms. Additionally, students should be trained on how to use these technologies effectively, ensuring they can fully participate in hybrid learning. -
3. Foster Collaboration with Parents
Hybrid learning success hinges on collaboration between teachers, students, and parents. Parents should be kept informed and engaged in their children’s learning, helping them navigate the new educational landscape. -
4. Design a Structured Curriculum
When designing a hybrid curriculum, it's important to blend both face-to-face and online elements effectively. Focus on creating clear learning objectives that guide both in-person and virtual activities. Use varied teaching approaches like collaborative and problem-based learning to engage students across both formats. -
5. Implement Assessment Strategies
Assessing students in a hybrid environment requires thoughtful planning. Use a combination of formative and summative assessments, incorporating tools that allow for peer reviews, self-assessments, and teacher feedback. Performance-based assessments such as presentations and projects are particularly effective in hybrid classrooms. -
6. Ensure Accessibility and Inclusion
Make sure the hybrid learning environment is accessible to all students. This includes providing captions for videos, using diverse teaching materials (written, audio, or video), and ensuring all students, regardless of their learning environment, can interact and engage effectively. -
7. Continuous Evaluation
Hybrid learning should be regularly assessed to ensure its effectiveness. Collect feedback from students and teachers to identify challenges and make adjustments to improve the experience.
The Future of Hybrid Learning: Advancements and Potential
The future of hybrid learning looks promising, with ongoing advancements in educational technology improving its effectiveness. As academic institutions adopt this model, they are investing in the necessary infrastructure to support flexible, blended learning environments. Technologies like AI are expected to enhance personalized learning, enabling coursework to be customized to meet individual needs. Virtual and augmented reality may also play a key role, offering immersive experiences that merge remote and in-person instruction. These innovations are setting the stage for hybrid learning to become a cornerstone of modern education.
Despite its advantages, hybrid learning faces challenges, particularly regarding its definition and full implementation. There is no single, clear understanding of what hybrid learning involves, leading to inconsistencies in its application. However, the benefits of this model—over traditional in-person or fully remote learning—are clear. As research and practices evolve, hybrid learning is likely to become more standardized and widely used, creating more inclusive and adaptable educational experiences.
Conclusion
Hybrid learning combines the best of in-person and online education, offering flexibility and personalized learning. While challenges like technology access and teaching strategies remain, its potential to shape future education is immense. With ongoing advancements in technology, hybrid learning is set to become a key framework in preparing students for a digital world.
Latest
Trends blogs
- From Vision to Impact: Closing the Gender Gap in STEM Education
- Automation, Artificial Intelligence, and the Future of Human-Centered Education
- Mid-Career Education in a Changing Labor Market
- The Next Phase of STEM Education: The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Classroom Curricula
Focus blogs
- Research-Driven Education: Strengthening Strategies, Policies, and Classroom Practice
- Professional Certifications for Career Growth: What Students and Young Professionals Need to Know
- Building a High-Impact Center of Excellence: What You Need to Know
- Beyond Graduation: The Importance of Lifelong Learning in Higher Education





