In today's increasingly diverse educational landscape, schools are embracing multiculturalism and multilingualism, welcoming students from various socioeconomic backgrounds. Recognizing the importance of students' holistic development, educators and community organizations are championing social and emotional learning (SEL) as a cornerstone of modern education.
As educators, it is crucial to understand the significance of SEL and its impact on students' academic and personal growth. By integrating SEL principles into the curriculum, teachers can create inclusive learning environments where students feel valued and supported. It empowers students to manage their emotions effectively, communicate empathetically, and collaborate productively with their peers.
Understanding Social Emotional Learning
Social-emotional learning (SEL) is an educational approach that focuses on nurturing students' social and emotional skills alongside academic learning. It involves teaching students to recognize and manage their emotions, develop empathy and social awareness, build positive relationships, and make responsible decisions.
At its core, SEL helps students better understand their emotions and express them appropriately, building a deeper level of self-awareness. By teaching students to recognize and manage their emotions, SEL empowers them to navigate challenging situations with resilience and empathy.
SEL also emphasizes the importance of building positive relationships and cultivating a sense of connection within the school community. Through collaborative activities and interpersonal skills development, students learn to communicate effectively, resolve conflicts peacefully, and work cooperatively with others.
Furthermore, SEL plays a crucial role in promoting inclusive learning environments and supporting students from diverse backgrounds. By cultivating empathy and understanding, it helps students appreciate diversity, embrace inclusivity, and develop compassion for others' experiences and perspectives.
By integrating SEL into education, schools create nurturing environments that empower students to thrive academically, socially, and emotionally, both in the classroom and beyond.
5 Essential SEL Components: The Key to Success
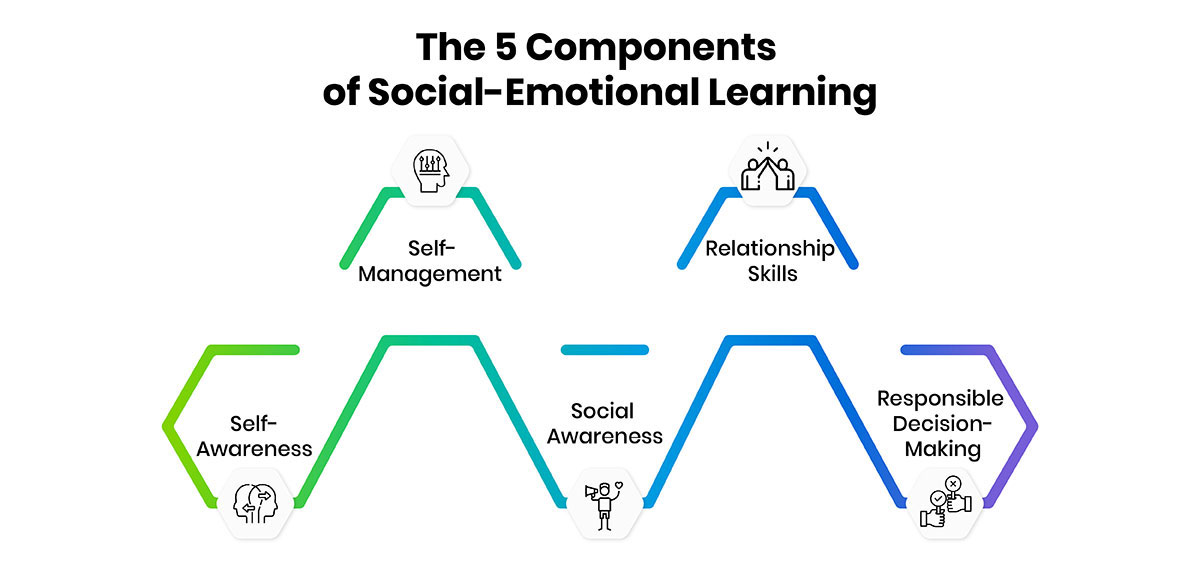
Social-emotional learning (SEL) is a vital aspect of education that encompasses five fundamental components or competencies that play a crucial role in helping students develop essential life skills and navigate various social and emotional challenges.
Here's a comprehensive overview of these components:
-
Self-Awareness:
Self-awareness is the foundation of social-emotional learning. It involves understanding one's own emotions, thoughts, and values, and how they influence behavior in different situations. Self-aware individuals can accurately assess their strengths and limitations, maintain positive mindsets, and possess a well-grounded sense of self-efficacy and optimism. -
Self-Management:
Self-management is closely linked to self-awareness and encompasses the ability to regulate one's emotions and behaviors effectively. This includes skills such as delaying gratification, managing stress, controlling impulses, and persevering through challenges to achieve personal and academic goals. Students with self-management can handle setbacks and maintain focus on their objectives. -
Social Awareness:
Social awareness involves understanding and empathizing with others, regardless of their background or culture. It entails recognizing social norms, demonstrating compassion, and acknowledging the resources and supports available within families, schools, and communities. -
Relationship Skills:
Relationship skills are essential for building and maintaining healthy connections with others. This competency encompasses effective communication, active listening, cooperation, conflict resolution, and seeking help when needed. Students with strong relationship skills can navigate diverse social dynamics, collaborate effectively, and foster positive relationships both inside and outside the classroom. -
Responsible Decision-Making:
Responsible decision-making involves making ethical, safe, and constructive choices across various contexts. It requires considering the impact of one's actions on oneself and others, evaluating risks and consequences, and adhering to ethical standards and behavioral norms. Students who demonstrate these skills are better equipped to navigate complex situations, solve problems, and contribute positively to their communities.
How Important is Social Emotional Learning?
The significance of Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) in education cannot be overstated. It serves as a foundational pillar for students' holistic development, furnishing them with life skills essential for success in both academic and personal spheres.
Fundamentally, SEL nurtures self-awareness, emotional regulation, and interpersonal competence. By facilitating a deep understanding of their emotions and thought processes, students can effectively manage their behavior, build resilience, and cultivate healthy relationships with others.
Moreover, SEL empowers students to navigate the complexities of the modern world with confidence and empathy. Through SEL, students learn problem-solving strategies, develop a sense of social responsibility, and become advocates for positive change in their communities. This proactive approach to personal and social development instills a sense of agency and purpose in students, preparing them to address challenges and seize opportunities in an ever-changing global landscape.
Additionally, integrating SEL into educational curricula benefits educators by creating a supportive learning environment; that is, teaching a classroom filled with SEL-equipped students who are conscientious, empathetic, and self-aware will be conducive to academic achievement and positive social interactions. SEL-equipped classrooms contains a culture of mutual respect, collaboration, and inclusivity, where students feel valued and empowered to express themselves authentically.
The Advantages of Social Emotional Learning
SEL offers numerous advantages for students, educators, and society. By nurturing the development of essential life skills and emotional intelligence, SEL contributes to various positive outcomes across different domains.
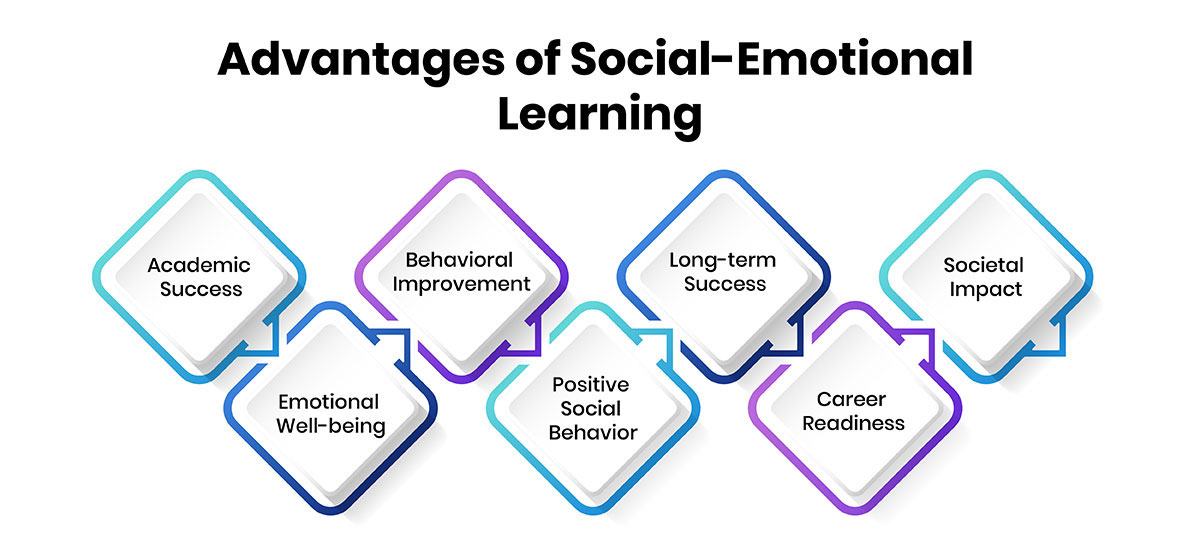
Here are the key advantages of social-emotional learning:
-
Academic Success:
- SEL enhances academic performance by improving students' engagement, motivation, and ability to focus in the classroom.- Research shows that students who participate in SEL programs demonstrate higher grades, improved attendance, and better test scores.
-
Behavioral Improvement:
- Students engaged in SEL exhibit fewer behavioral problems, such as aggression and disobedience, leading to a more conducive learning environment.- SEL equips students with the skills to manage their emotions, resolve conflicts peacefully, and exercise good judgment, reducing disruptive behaviors.
-
Emotional Well-being:
- SEL programs help students develop resilience, cope with stress, and manage their emotions effectively, leading to reduced anxiety, depression, and emotional distress.- By promoting self-awareness and empathy, SEL supports better relationships and a sense of belonging, enhancing overall emotional well-being.
-
Positive Social Behavior:
- SEL encourages positive social interactions, empathy, and respect for others, creating a culture of kindness and inclusivity within schools.- Students who participate in SEL demonstrate enhanced communication skills, teamwork abilities, and conflict resolution strategies, contributing to positive peer relationships.
-
Long-term Success:
- The benefits of SEL extend beyond the classroom, influencing students' long-term outcomes and success in adulthood.- SEL nurtures skills such as self-regulation, compassion, and rational decision-making, which are essential for career success, strong relationships, and overall well-being.
-
Career Readiness:
- Employers recognize the value of social-emotional skills in the workplace, making SEL an integral part of career readiness and professional development.- Students who develop SEL competencies are better equipped to navigate complex social dynamics, collaborate effectively, and adapt to diverse work environments.
-
Societal Impact:
- SEL contributes to creating a more compassionate and empathetic society by nurturing individuals who value social justice, diversity, and community engagement.- As SEL becomes ingrained in educational practices, it has the potential to reduce societal issues such as crime, poverty, and inequality, leading to a more equitable and harmonious society.
Implementing SEL in Classrooms
Implementing SEL in classrooms requires a thoughtful and comprehensive approach that integrates SEL practices into teaching and learning.
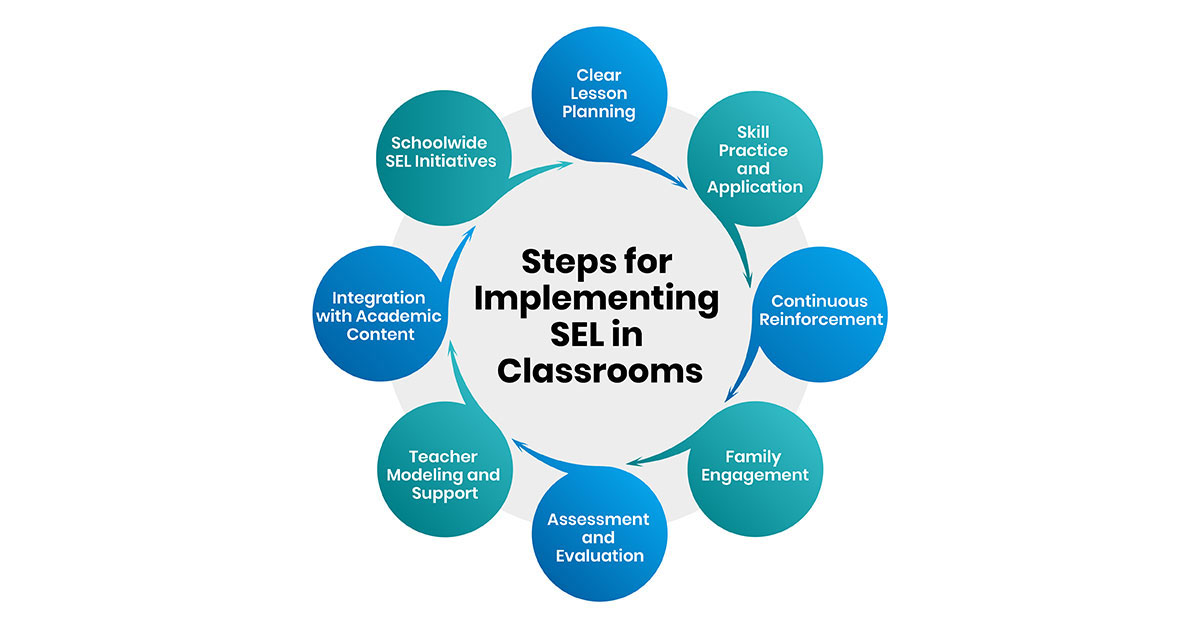
Here are some strategies for effectively incorporating SEL into the classroom:
-
Clear Lesson Planning:
Begin by creating clear lesson plans that explicitly teach social-emotional skills. Introduce SEL concepts to students using a variety of instructional methods, such as visuals, videos, discussions, and written texts. -
Skill Practice and Application:
Provide opportunities for students to practice and apply social-emotional skills in various contexts. This could involve group activities, role-playing scenarios, or individual reflection exercises. Encourage students to apply SEL skills in real-life situations. -
Continuous Reinforcement:
Reinforce SEL concepts and skills consistently throughout the school year. Revisit and review SEL topics regularly to ensure that students are internalizing and applying what they have learned. Use positive reinforcement and feedback to motivate students and acknowledge their progress. -
Family Engagement:
Involve families in the SEL process by providing homework assignments or activities that students can complete with their families. Encourage parents and caregivers to reinforce SEL skills at home and support their child's social-emotional development. -
Assessment and Evaluation:
Assess students' understanding and application of SEL skills through formative and summative assessments. Use observation, self-assessment, and peer feedback to evaluate students' social-emotional competencies. Adjust instruction and support based on individual student needs.| Also Read - 5 Essential Types of Assessments in Education
-
Teacher Modeling and Support:
Model positive social-emotional behaviors and attitudes for students through your own interactions and communication. Create a supportive classroom environment where students feel safe to express themselves and take risks. -
Integration with Academic Content:
Integrate SEL practices into academic subjects such as English language arts, social studies, math, and science. Use literature, historical events, and real-world examples to teach SEL concepts and reinforce academic learning. -
Schoolwide SEL Initiatives:
Collaborate with school leaders and colleagues to develop schoolwide SEL initiatives and policies. Establish clear expectations and norms for SEL implementation across all grade levels and classrooms. Provide professional development and support for educators to enhance their SEL teaching practices.
Conclusion
SEL prepares students with essential skills for success in academics, relationships, and life. By integrating SEL into classrooms, educators create nurturing environments where students thrive emotionally and academically. With SEL, laying the foundation for a brighter future filled with endurance, benevolence, and success is a promise.
Latest
Trends blogs
- From Vision to Impact: Closing the Gender Gap in STEM Education
- Automation, Artificial Intelligence, and the Future of Human-Centered Education
- Mid-Career Education in a Changing Labor Market
- The Next Phase of STEM Education: The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Classroom Curricula
Focus blogs
- Research-Driven Education: Strengthening Strategies, Policies, and Classroom Practice
- Professional Certifications for Career Growth: What Students and Young Professionals Need to Know
- Building a High-Impact Center of Excellence: What You Need to Know
- Beyond Graduation: The Importance of Lifelong Learning in Higher Education





