Cybersecurity has become a critical concern for educational institutions, especially as cyberattacks on colleges and universities have escalated in recent years. With a significant increase in remote learning and digital integration, educational institutions have become prime targets for cybercriminals. The alarming frequency of ransomware attacks, which have affected a considerable number of schools, underscores the urgency of securing sensitive data, including student and employee information, intellectual property, and institutional records. As the education sector grapples with these growing threats, the imperative to protect not only financial assets but also the privacy and safety of students and staff has never been more pressing.
The Importance of Cybersecurity in Education
The importance of cybersecurity in education has never been more critical, given the rapid digital transformation within educational institutions and the alarming rise in cyberattacks. The State of Ransomware study finds out that, a staggering 79% of schools reported falling victim to ransomware attacks, with over half of them paying a ransom to recover their data the same year. This highlights the urgent need for robust cybersecurity measures to protect not only the operational integrity of these institutions but also the privacy and safety of students, teachers, and administrators. As millions of students now rely on technology for hybrid, remote, or in-class learning, securing their devices and the digital environments in which they operate has become paramount.
Educational institutions are custodians of vast amounts of sensitive data. This makes them prime targets for cybercriminals who seek to exploit this data for identity theft, fraud, or even blackmail. The threat is further exacerbated by the widespread adoption of online learning platforms and digital tools, which has significantly expanded the digital footprint of these institutions. For example, the EdTech magazine’s report on malware attacks in higher education, reveals a staggering 105% surge in reported ransomware incidents targeting both K–12 and higher education institutions, illustrating the scale of the threat.
With the frequency and sophistication of cyberattacks steadily increasing, educational institutions must prioritize cybersecurity to protect their digital infrastructure. This is not only about preventing economic losses or operational disruptions but also about ensuring the privacy and well-being of students, particularly minors in K–12 settings. By implementing comprehensive cybersecurity strategies, educational institutions can create a secure learning environment where students can engage with technology safely, and teachers and administrators can perform their duties without the constant threat of cyber intrusions. Ensuring that all stakeholders are protected against cyber threats is a fundamental responsibility that is crucial to maintaining trust, safety, and the integrity of the educational process.
Common Cyber Threats Targeting Educational Institutes
Educational institutions are increasingly becoming high-priority targets for cybercriminals due to the extensive handling of confidential information, including personal information, academic records, and financial details. The transition to digital and remote learning, has further exposed vulnerabilities in educational networks, leading to a significant rise in cyberattacks.
Among the most common threats are ransomware attacks, where cybercriminals encrypt institutional data and demand a ransom for its release. These attacks can lead to severe operational disruptions, even in academic plans and potential financial losses. Additionally, data breaches in educational institutions can result in the unauthorized access and exposure of sensitive information, putting students, staff, and faculty at risk of identity theft and other forms of exploitation.
Phishing schemes also represent a substantial threat, with attackers using deceptive emails or messages to trick individuals into divulging login credentials or clicking on malicious links. Such tactics often lead to further breaches and can compromise entire networks.
Moreover, the education sector's general lack of cybersecurity training and resources escalate these risks. Many institutions have not yet fully implemented robust security measures, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals. Ensuring the safety of digital environments in schools and universities is essential to protecting the privacy and security of all stakeholders involved.
The Impact of Cyberattacks on Educational Institutions
Cyberattacks have a profound impact on educational institutions, disrupting their operations and compromising the security of critical data. When schools and universities are targeted by ransomware, they can face significant downtime, leading to canceled classes, delayed academic schedules, and even the loss of critical data. These disruptions can severely affect the learning environment, hindering students' education and educators' ability to teach effectively.
Data breaches pose another severe consequence, where personal information, such as student records, staff details, and financial information, can be exposed or stolen. This not only jeopardizes the privacy of individuals but also opens the door to identity theft and fraud. The financial implications are substantial as well, with institutions potentially facing legal liabilities, loss of trust from stakeholders, and the cost of recovering from such attacks.
The reputational damage resulting from a cyberattack can be long-lasting. Parents, students, and staff may lose confidence in the institution's ability to safeguard their data, which can lead to decreased enrollment and difficulties in maintaining donor and alumni support. So, the need for robust cybersecurity measures becomes ever more critical to protect against these escalating threats.
Best Cybersecurity Practices To Adopt
In the realm of education, safeguarding students and faculty from cyber threats requires a multi-faceted approach. Here’s a guide to implementing effective cybersecurity practices:
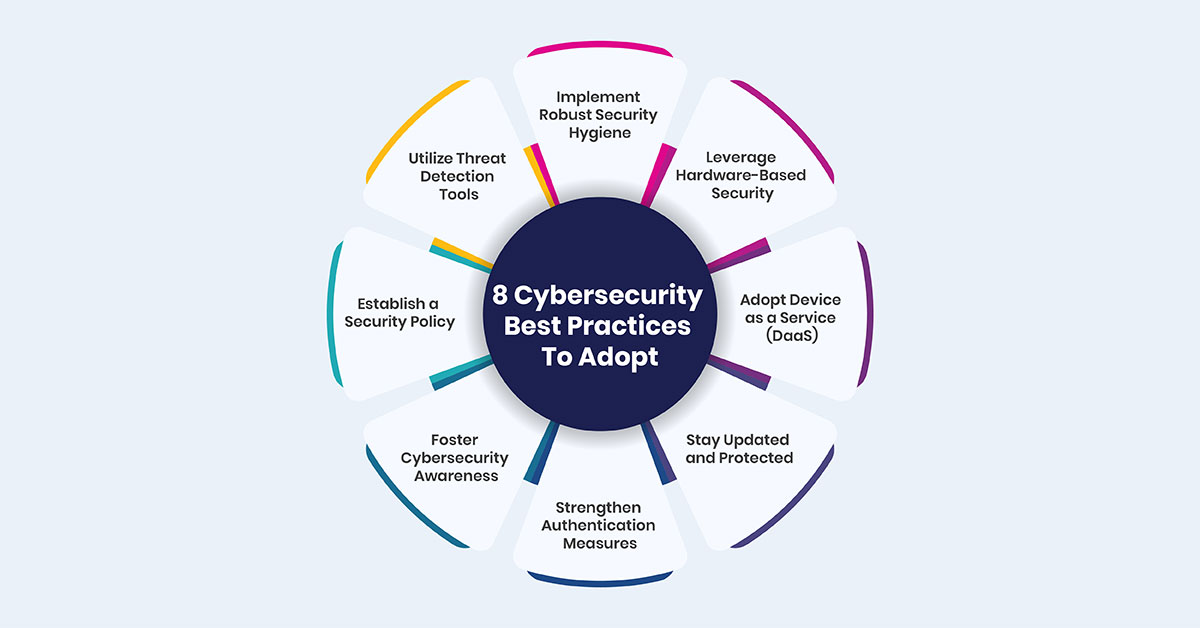
-
1.Implement Robust Security Hygiene
Educating younger students about online risks is crucial. Introducing cybersecurity concepts early on can significantly reduce the likelihood of falling victim to attacks. Various Online Safety Programs for Kids provide valuable resources such as age-appropriate presentations and quizzes to help children understand and navigate potential cyber threats. -
2.Leverage Hardware-Based Security
Relying solely on software-based defenses can leave systems vulnerable to deeper threats. Integrating hardware-based security solutions helps protect against attacks that exploit vulnerabilities beneath the operating system. Numerous platforms offer advanced features, enhancing device protection by reducing attack vectors and improving overall security resilience. -
3.Adopt Device as a Service (DaaS)
Embracing a Device as a Service (DaaS) model can streamline device management while bolstering security. DaaS solutions, provide comprehensive device management and technical support, including advanced security features. This approach not only optimizes IT resources but also ensures consistent protection and support across all user devices. -
4.Stay Updated and Protected
Regularly updating software is essential to close security gaps and prevent exploitation by cybercriminals. Ensure that all systems are patched with the latest updates to defend against known vulnerabilities. Additionally, installing anti-malware and anti-virus software with automated updates and real-time scanning capabilities is crucial for blocking malicious threats. -
5.Strengthen Authentication Measures
Employing strong, complex passwords is a fundamental step in protecting institutional accounts. Use passwords that incorporate a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols to enhance security. Multi-factor authentication should be enabled for remote access to add an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access. -
6.Foster Cybersecurity Awareness
Conducting regular cybersecurity training for students, staff, and faculty is vital. Awareness programs should cover common threats such as phishing, ransomware, and business email compromise, and provide practical advice on recognizing and avoiding these attacks. Training should also extend to safe data-handling practices and secure use of technology. -
7.Establish a Security Policy
Develop and maintain a comprehensive IT security policy that outlines acceptable behaviors, responsibilities, and procedures for safeguarding digital assets. This policy should address emerging threats and compliance requirements as well as integrate guidelines for managing risks associated with AI and ensure regular updates to adapt to new challenges. -
8.Utilize Threat Detection Tools
Invest in early threat detection and monitoring tools to identify and mitigate risks before they escalate. Technologies such as data loss prevention software can provide real-time threat analysis and help prevent breaches, ensuring a proactive stance against potential security incidents.
Practical Approaches to Implementing Cybersecurity Measures
Institutions can build a strong cybersecurity framework to protect against digital threats when it is implemented rightly. Let’s look at the steps to be taken:
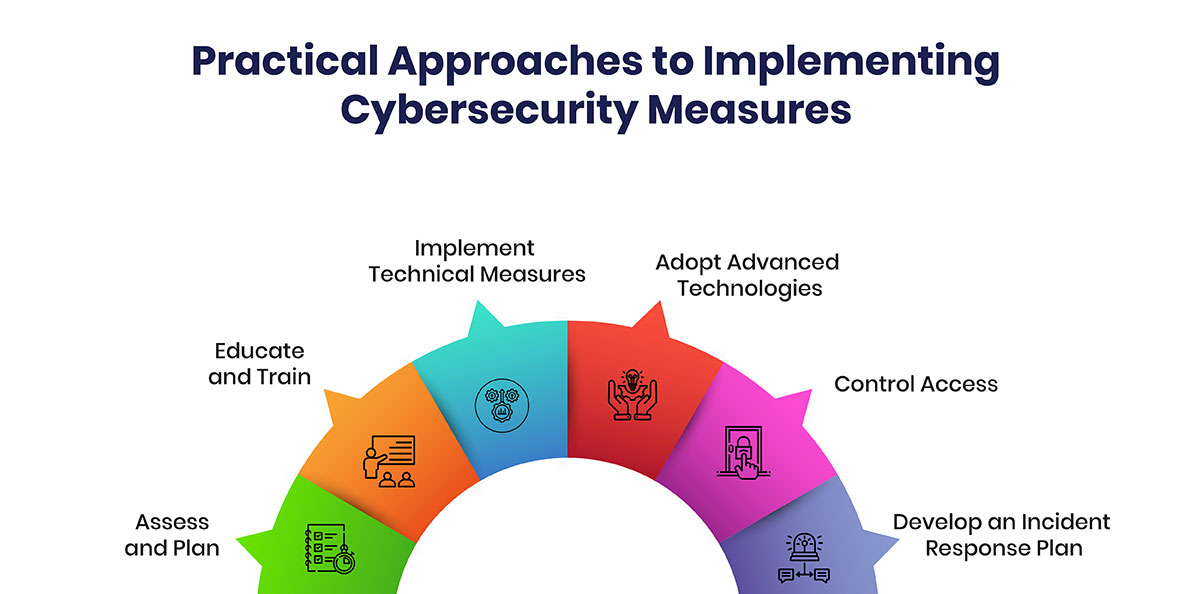
-
1.Assess and Plan
Evaluate Risks: Conduct a risk assessment to identify vulnerabilities. Create a Cybersecurity Plan: Set clear goals and establish a comprehensive IT security policy. -
2.Educate and Train
Awareness Programs: Regularly train staff and students on cyber threats and safety practices. Promote Cyber Hygiene: Encourage strong passwords and safe internet use. -
3.Implement Technical Measures
Install Security Software: Use anti-virus, firewalls, and regularly update all systems. Enable MFA: Use multi-factor authentication for critical access. -
4.Adopt Advanced Technologies
Use Hardware-Based Security: Implement secure processors and encryption. Monitor Networks: Invest in real-time threat detection tools. -
5.Control Access
Limit Data Access: Restrict access to sensitive data based on roles. Review Permissions: Regularly check user access rights. -
6.Develop an Incident Response Plan
Create a Response Team: Prepare for cyber incidents with a dedicated team and regular drills.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of cybersecurity in education requires a proactive and layered approach. As the digital landscape evolves, so do the methods of those who seek to exploit it. Ensuring that educational institutions are equipped with both the knowledge and tools to defend against cyber threats is essential for maintaining not only operational continuity but also the trust and safety of the entire academic community. Investing in these areas is not just a precaution; it is a fundamental responsibility in today’s interconnected world.
Latest
Trends blogs
- From Vision to Impact: Closing the Gender Gap in STEM Education
- Automation, Artificial Intelligence, and the Future of Human-Centered Education
- Mid-Career Education in a Changing Labor Market
- The Next Phase of STEM Education: The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Classroom Curricula
Focus blogs
- Research-Driven Education: Strengthening Strategies, Policies, and Classroom Practice
- Professional Certifications for Career Growth: What Students and Young Professionals Need to Know
- Building a High-Impact Center of Excellence: What You Need to Know
- Beyond Graduation: The Importance of Lifelong Learning in Higher Education





